In our digital age, every business knows how important data is. Companies across all industries heavily rely on data to make accurate predictions and strategic decisions. But the problem is that, as your business grows, you get flooded with data from multiple sources.
Customers are everywhere, and there are so many different databases which store information about them. If you’re still gathering those data manually in an Excel sheet, you’re not only wasting time, but you’re also susceptible to lots of errors.
That’s where a Customer Data Platform (CDP) comes in handy. In this article, we’ll explain what customer data platforms are, how you can benefit from implementing them, and how to choose the right CDP for your business.
What Is a Customer Data Platform (CDP)?
A customer data platform is a technological solution that collects, stores, and analyzes customer data to help businesses make better decisions.
A CDP unifies data from multiple sources into one place so that companies can gain a more composite overview of their data. This can help them improve their interactions with customers in real time, make predictions, or identify possible issues.
As an eCommerce business, your customer data is spread across multiple touch points and sources – and a CDP is essentially a repository that stores and organizes all of that dispersed data into one, unified whole.
For example, a customer might find your store via a quick Google search on their mobile phone. Then, they check out your website and browse through your product catalog, but don’t take any action. This same customer might come back to your store a few days later on their laptop and sign up for your newsletter. A few days or weeks later, they might return to add a few products to their cart and make a purchase.
Without a CDP, all this data would remain stored in various places, making it hard for you to piece together this customer’s entire journey.
You’d only know that they signed up for your newsletter and made a purchase, but you won’t know how many times they interacted with your website before taking action.
With a CDP, however, you’ll be able to view all those single data points as a cohesive customer profile, allowing you to gain more insights into how they interact and engage with your brand.
You can then use this data to enhance your marketing campaigns, create more personalized customer experiences, target the right audience segments with the right messages, and improve your conversion rates.
What does a CDP do?
A customer data platform (CDP) works with data in four steps:

1. Data collection
It collects data from multiple sources, such as your website, CRMs, social media, and other marketing touchpoints. This data is then stored in one place.
2. Data unification
It unifies and organizes recollected data.
A CDP links the data about the same customer from multiple sources, creating a single customer profile that includes demographics, behavior, purchase history, and more.
3. Data activation
It activates the data to make it available to all members of your team. CDPs make customer data available to other systems and teams, such as marketing automation, analytics, and CRM systems.
This allows your teams to provide more personalized and relevant customer experiences.
4. Data analysis
It analyzes data about that customer. Having all the data about one customer recollected and unified, the platform can now analyze this data to gain insights into the customer’s behavior and preferences.
You can use these insights to improve your marketing and sales campaigns, make predictions, or personalize customer interactions.
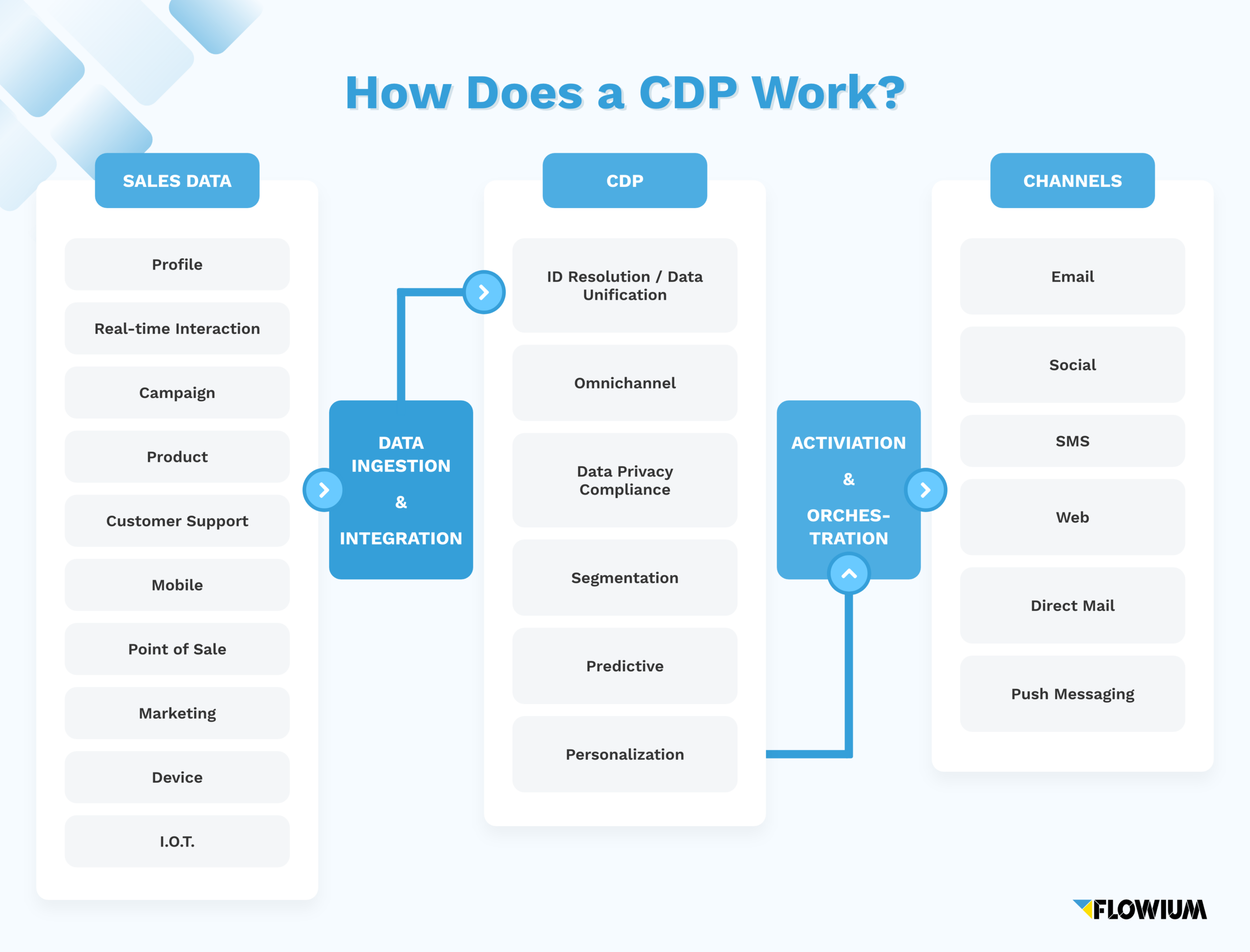
How does a CDP work?
Customer data platforms typically use a variety of methods to pull data from different sources, clean this data, and analyze it to create unified customer profiles. CDPs connect to various data sources and use data connectors, APIs, and SDKs to pull various data, such as behavioral, transactional, product data, campaign, and other relevant data.
After the data is collected, the CDP uses data ingestion to clean and format the data so that it can be easily integrated with the rest of the data into one single customer profile through data matching.
Once the data is unified, CDPs then use methods such as machine learning, statistical modeling, and segmentation to analyze this data and come up with detailed insights about the customer and uncover behavioral patterns.
What data does CDP collect?
A customer data platform gathers a wide variety of customer data from various sources. It can be divided into first-party data (data collected by the company directly from the customer) and third-party data (data purchased from other companies or sources).
Typically, the data that a CDP collects about your customers can be grouped into four data categories:
- Demographic data: This includes information such as age, gender, and location.
- Behavioral data: This includes what products or services people buy from you, as well as when and where they buy them.
- Interaction data: This includes information about how people interact with you via different marketing channels, such as your website or app. This means any interaction between a customer and an item of interest within your business. It can be, for example, a click on a specific ad or an online purchase through an eCommerce website.
- Transactional data: This refers to the details of every transaction between you and your customers and covers everything from payments to emails to shipping confirmations is considered transactional data.
Common CDP use cases
Businesses often use CDPs for two main purposes: to create more personalized customer experiences and to improve their targeting and prospecting efforts.
Some of the most common use of a CDP are:
- Personalization: Because a CDP collects data from multiple sources and uses it to create unified customer profiles, it helps companies create a more personalized experience for each customer.
- Segmentation: A CDP helps companies collect and analyze data about customer behavior and preferences, which can be used to segment customers into groups based on shared characteristics
- Analytics & Insights: Because a CDP tracks customer interactions across multiple marketing touchpoints, it can help you identify how your marketing campaigns are performing.
- Marketing Automation: With a CDP, you can set up automated outreach campaigns based on triggers. This enables companies to reach out to the right customers at the right time.
- Predictive Modeling: A CDP can also be used to build predictive models that predict customer behavior, such as the likelihood of churning or purchasing.
- Lookalike Audiences Building: A CDP allows you to identify and analyze the characteristics of your target audience. You can then use this data to create buyer personas or lookalike audiences.
CDP vs. DMP vs. CRM
Customer data platforms (CDP), data management platforms (DMP), and customer relationship management systems (CRM) are tools that help businesses analyze and manage customer data to improve their customer interactions.
These terms can be pretty confusing because of how similar they appear to be at first glance. However, they have distinct functions and features. Let’s explain what each of these tools does.
A CDP is not a DMP nor a CRM
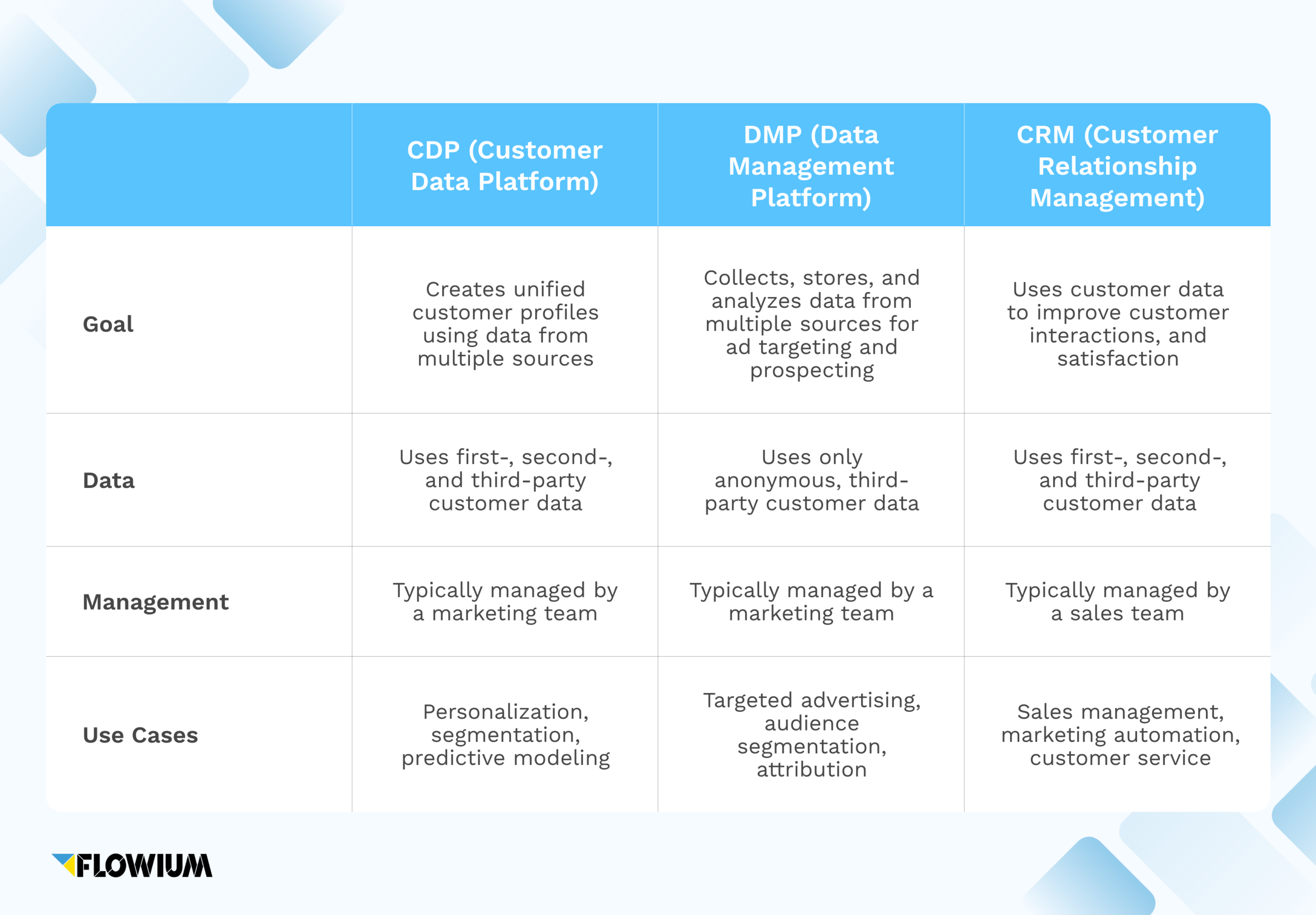
A customer data platform (CDP) is a tool that allows companies to collect, store and analyze data from multiple sources — including online and offline channels. The main goal of a CDP is to unify data to create accurate customer profiles.
A data management platform (DMP) differs from a CDP in that it’s used specifically for targeting purposes and uses only anonymous, third-party data. The goal of a DMP is also to collect, store, and analyze data from multiple sources. But, unlike a CDP, a DMP doesn’t use this data to enable customer modeling. It uses this data to improve ad targeting and content personalization.
Out of these three tools, the customer relationship management system (CRM) is the one that differs the most from the other two. A CRM helps businesses optimize their processes to increase customer satisfaction. In other words, a CRM helps companies manage customer interactions and track them throughout the customer lifecycle.
CDP vs. DMP vs. CRM: Comparison tab
Customer data platforms (CDPs), data management platforms (DMPs), and customer relationship management systems (CRMs) are all technologies that are used to help companies collect and store customer information. But they each have unique features and capabilities, so it’s important to understand the differences between them.
Here’s a quick comparison highlighting the key differences between a CDP, DMP, and CRM:
Benefits of a Customer Data Platform for an eCommerce
A customer data platform (CDP) is a single source of truth for all customer data, including transactional and behavioral. As such, it serves as the foundation for strengthening the customer experience and driving revenue growth.
A CDP enables companies to connect every customer touchpoint into a single view of the customer. A CDP is critical for enterprises that want to create personalized experiences for their customers across marketing, sales, and service channels in real time.
Let’s look at some of the main benefits of a CDP for eCommerce.
Better customer data management
Customer data platforms help businesses manage both internal and external customer data in one place.
This allows them to consolidate all relevant information related to each customer, regardless of whether it comes from different departments within the company or external sources like social media or third-party data providers.
Since a CDP is a central depository of all the customer data in one place, it makes it easy for businesses to share information with other departments within their organization – such as sales teams or customer service representatives – so everyone is working together towards the same goal: improving the customer experience and increasing revenue.
Better customer analytics
A CDP gives a holistic view of all customer data across channels and devices. This means you can see how every touchpoint — from email to live chat — contributes to your overall goals.
Having all this information in one place makes it easier to see how each interaction affects customer experience and loyalty.
For example, if you notice that a certain type of message drives more conversions or repeat purchases, you can optimize your message strategy around that insight.
A CDP also allows you to test new methods of reaching customers before you make permanent changes across all channels.
Better data and privacy protection
Thanks to a CDP, businesses are able to safely meet all the security standards for handling personal information by using identity resolution and data masking capabilities.
CDPs allow marketers to ensure compliance with how customer data is used across all touchpoints while also using it for marketing purposes.
This can help companies avoid fines and penalties from regulators such as the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
CDPs also make it easier for customers to control how their data is used by providing them with access to their personal information.
They can choose which pieces of data they want to share with businesses, whether it’s their email address or location or preferences in products or services.
Better segmentation & personalization
Customer data platforms help businesses segment their customers into groups based on common characteristics such as demographics, psychographics, and behaviors.
These groups can be targeted with specific marketing campaigns catering to their needs.
For example, a company might use its customer data platform to send tailored ads for specific products based on past purchases or website activity.
Having deeper insights into your customers and being able to segment them based on their preferences leads to more personalized content across all marketing touchpoints.
This ensures your content resonates with each target group at precisely the right time so that every message is relevant. In turn, this can help drive more sales leads and conversions.
How to Choose a CDP
A CDP serves as an always-on, real-time data hub for your entire organization. It’s a single place where you can store and access all of your customer information — regardless of whether it resides in your CRM system, marketing automation tool, or elsewhere in your enterprise.
Choosing a CDP for your business isn’t an easy task. Yet, selecting the right one is crucial to your business.
If you choose poorly, you could end up with a system that doesn’t meet your needs.
Currently, there are more and more customer data platforms to choose from, and it can be challenging to figure out which one fits your business needs the most.
Below, we share the most practical tips for selecting the right CDP for your business.
Questions to ask yourself before choosing a CDP
Before choosing your CDP, there are a few questions you need to ask yourself to determine whether it’s the right fit for your business.
Question 1: How does this CDP fit the needs of your business as a whole?
The CDP you choose will have an impact on your entire organization. That’s why it’s important to understand how it fits into your organization’s overall strategy and how well it aligns with the needs of each team or department that will use it in the future.
The first thing you need to consider before choosing a CDP is who will use it and how.
For example, your sales team may collect data from your CRM, while your social media marketing team may collect data from social media platforms such as Facebook or Instagram.
If you have an SEO team, they’re likely collecting data from SEO and analytics tools, such as Google Analytics or SEMRush.
To choose the right CDP, you need to consider the goals and expectations of each team that currently collects and handles data in your company.
Question 2: What will you use this CDP for?
The next thing you need to consider before selecting a CDP for your business is how you plan on using it.
You may be looking for a CDP because it’ll help you consolidate data into one omnichannel repository. However, centralizing data isn’t the final result you can obtain from implementing a CDP into your business, but rather just the beginning of what you can gain from it.
The most common reasons why companies use a CDP include:
- Creating a more personalized customer experience to increase customer satisfaction
- Gaining deeper insights into your customers’ journey to better understand them
- Improving your ad targeting to increase conversions
- Predicting customer behavior and interactions to create more targeted marketing campaigns
Knowing exactly what you expect from your CDP will help you determine which platform fits best with your needs.
Question 3: What tools will you need this CDP to integrate with?
Another thing to consider before choosing a CDP is what tool you need it to integrate with.
In an eCommerce business, different teams use different tools to collect data – and your CDP needs to fit well with all of them. The most common data collecting tools you may need your CDP to integrate with are:
- Google Analytics
- Facebook Pixel
- CRM software
- Email marketing software
- Live chat and customer success tools
- Point-of-sale (POS) systems
- Social media analytics tools
The right CDP for your business will be able to connect to the most important data collecting tools you already use in your business.
Features to look for in a good CDP
A CDP isn’t just about gathering data in one place. Most CDP platforms have features that go beyond collecting and storing data.
Think about what you expect your CDP to help you with. Here are some of the most common features a CDP should have:
- Data integration: Collect, store, and analyze data from multiple sources relevant to your business, such as website analytics, social media, CRM, and offline data sources like point-of-sale systems
- Identity resolution: Gain a cohesive overview of your customers’ journey
- Data governance: Stay compliant with data privacy and protection protocols, such as GDPR and CCPA
- Data security: Protect customer data from unexpected breaches or leaks, thanks to security protocols such as ISO 27001 or SOC 2
- Data segmentation: Effectively segment your customer into groups based on similar characteristics thanks to data segmentation capabilities
Before choosing a CDP, consider your non-negotiable requirements and make a list of features you need it to have.
Best Customer Data Platform for eCommerce: Klaviyo One
As your eCommerce business grows, the need for a customer data platform (CDP) becomes more and more critical, and choosing the right one is crucial to your business’s success.
With so many CDPs, it’s important to choose one specifically designed for eCommerce businesses, such as Klaviyo One.

Klaviyo One is an excellent choice of CPD for an eCommerce business because it offers several features tailored to the specific needs of eCommerce businesses.
Aside from all the features of a typical CDP, such as identity resolution, segmentation, and data governance, Klaviyo One has been specifically designed to collect and analyze data specific to eCommerce businesses.
This data includes purchase history, product browsing behavior, and cart abandonment, just to name a few.
In addition, Klaviyo One can integrate with popular eCommerce platforms such as Shopify, Magento, and BigCommerce, making it easy to collect and analyze data from these platforms.
FAQs about Customer Data Platforms
The acronym CDP stands for customer data platform, which is a tool that helps businesses gather customer data from various sources, analyze it, and create detailed customer profiles.
No, Google Analytics is not a CDP. While Google Analytics is the most common tool for tracking website activity, it’s not a CDP, as it doesn’t consolidate data from multiple sources into one place.
No, a CDP is not a CRM. A CDP gathers and analyzes customer data to create customer profiles, while a CRM helps businesses optimize customer-related processes, such as contact management and customer service.







