The Net Promoter Score metric (NPS) was introduced in 2003 by Fred Reichheld of Bain & Company, through his best-selling book “The Ultimate Question: Driving Good Profits and True Growth”.
Reichheld created NPS as a new way to measure customer loyalty generated by the experience offered by a business, and it has become the gold standard Customer Experience Metric.
Today, more than two-thirds of the Fortune 1000 list use NPS to determine customer loyalty, including brands such as Apple, Intuit, GE and American Express.
In this guide we’ll look at net promoter score definition and the meaning of NPS, the different types of NPS, how to calculate net promoter score, and some examples.
What Is Net Promoter Score? (NPS)
So what is NPS’ meaning? The NPS (Net Promoter Score) is a customer experience metric used to measure customer loyalty.
It ranges from -100 to 100 and is used to determine the willingness of the customer to recommend the business, products or services to others.
NPS will help you gauge:
- Customer satisfaction levels
- Growth potential
- Customer experience quality
- Brand perception
- Organizational performance
Typically distributed in a survey form, the main question is usually a form of this single question:
How likely are you to recommend [Company] to a friend or colleague?
0 is Not Likely, and 10 is Very Likely.
The NPS enables a business to benchmark the loyalty of its customers and predict their purchase and referral behavior.

Why is Net Promoter Score Important?
The Nielsen Global Trust in Advertising Report identified that 83% of online respondents trusted the recommendation of friends and family.
This highlights the importance of recommendations and reviews when deciding any spending in general.
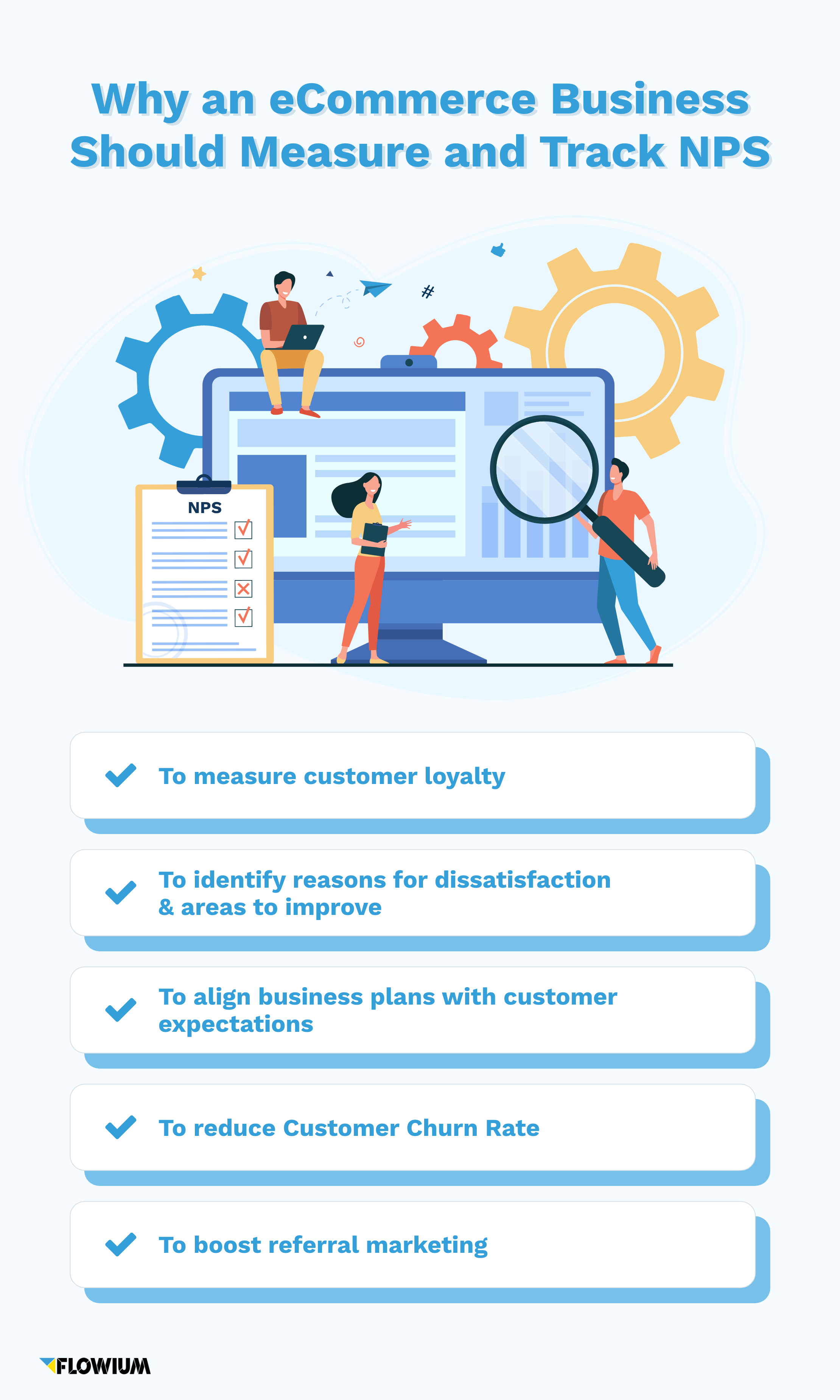
There are many reasons a business should measure and track NPS, and a few important examples are:
- To measure customer loyalty
- To identify reasons for dissatisfaction & areas to improve
- To align business plans with customer expectations
- To reduce Customer Churn Rate
- To boost referral marketing
To measure customer loyalty
Loyalty is an important determinant for customers to continue doing business and also increasing their spending with the company in question.
As a metric, it’s hard to measure, and most companies determine customer loyalty by measuring repeat purchases, average order value, referrals and churn rate. However, none of these are direct indicators of loyalty.
💡 By regularly measuring NPS, a business can not only quantify customer loyalty, but also compare it over a period of time to fuel understanding of business health and growth.
To identify reasons for dissatisfaction & areas to improve
While measuring NPS alone doesn’t identify reasons for the dissatisfaction of passives and detractors, NPS Surveys can be used to obtain both quantitative and qualitative data.
Follow up, open-ended questions can help identify issues and work towards closing the feedback loop.
To align business plans with customer expectations
Qualitative customer feedback will help identify what improvements and features customers expect from a business.
By following up an NPS question with something like ‘What can we change to make your experience better?’ customers are likely to share suggestions which can be analyzed and give insight into their expectations.
💡 By aligning business plans with customer expectation, we can convert detractors into promoters.
To reduce customer churn rate
Churn refers to a customer not repurchasing, canceling their account or renewal, or moving to a different business.
It is more expensive to acquire a new customer than to retain an existing one, so by increasing customer retention we can increase profits. By measuring NPS, we can determine which customers are likely to churn.
By studying NPS trends we can also identify an increase or decrease in detractors, passives and promoters, to give an indication of the health of the business’s relationship with customers.
A decrease in detractors and increase in passives will suggest a positive trend has begun. The goal should be to gradually convert those passives to promoters.
To boost referral marketing
92% of consumers say they trust recommendations above all other forms of advertising.
By using NPS Surveys to identify your promoters, these can be leveraged by seeking testimonials, case studies and referrals.
💡 NPS makes it much easier to identify the happy customers you can collaborate with in marketing the business or brand.
How To Calculate Net Promoter Score?
To understand how to calculate net promoter score, we first need to understand the question, the scale and its components.
The customer rates their willingness to recommend the company and/or its products and services on a scale of 0-10.
The response will put the customer into one of three categories:

Promoters (scores of 9 or 10)
These customers are very loyal to the company and are most likely to recommend you to peers.
Promoters act as brand ambassadors, make recurring purchases and contribute to word-of-mouth marketing.
Passives (scores of 7 or 8)
These customers are moderate towards the company, and may switch if a better option is given by a competitor brand. They are typically satisfied but uninvolved.
Detractors (scores of 0 to 6)
These customers are disloyal to the company and likely to speak negatively of it.
Detractors are unsatisfied customers who won’t buy from the company again, and are likely to switch to the competition. Their negative opinions might drive potential customers away.
By subtracting the percentage of Detractors from the percentage of Promoters, we determine the Net Promoter Score, which will range from -100 to 100.
If detractors outnumber promoters, the score will be less than 0. A good NPS is achieved by having more promoters than detractors, and therefore a score greater than 0.
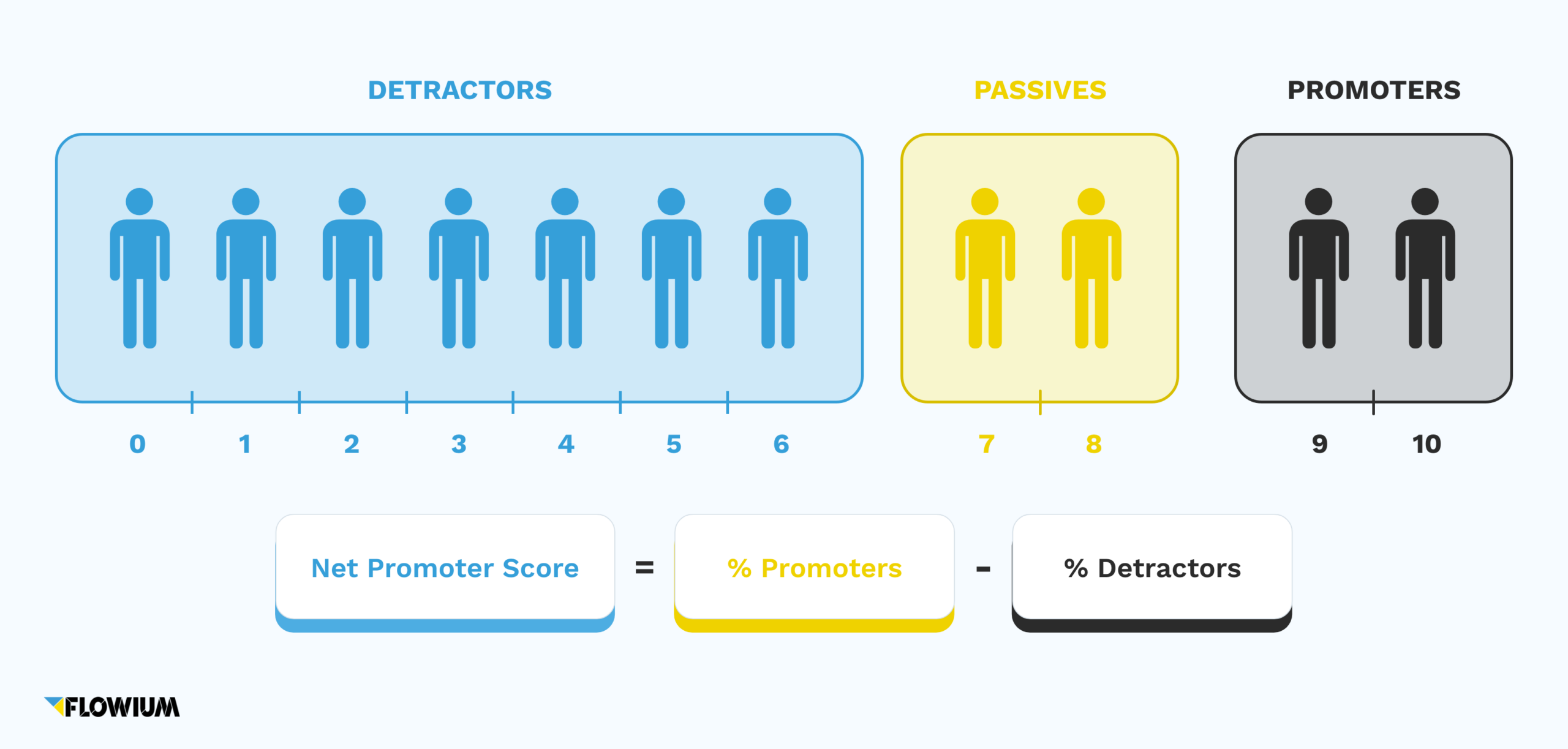
Net promoter score formula:
NPS = % Promoters – % Detractors
We can calculate net promoter score in several ways:
- In an Excel spreadsheet
- Using a free online calculator
- With NPS software
💡 Remember: Net Promoter Score is expressed as an integer between -100 and +100, not a percentage.
Examples of NPS Survey Questions
It’s important to decide on follow-up questions to ask customers, depending on their score. Just like face-to-face conversations, the wording, tone and phrasing of the question will impact the response.
Generally, an NPS survey is a simple questionnaire that aims to predict whether the customer will repurchase or refer it to someone else.
The first part of a survey will ask the customer to rate the business/product/service on a scale of 0-10. The second part is a follow-up, open-ended question as to why the specific score was given.
Let’s look at some net promoter score question examples.

Net promoter score survey questions
When first getting started with Net Promoter Score surveys it’s a good idea to use the default survey question. This is simply:
“On a scale of 0-10, how likely are you to recommend our business to a friend or colleague?”
This simple question is designed to capture the customer’s satisfaction with the business. It will help establish the foundation of communication with customers, and offers them the opportunity to speak their minds.
This rating question is effective at measuring customer loyalty, tracking the results of a particular marketing campaign, and supporting long-term growth strategies.
It’s a good icebreaker to open communication channels with customers, and will provide a consistent overview of the company and insights into issues across departments.
We can make the classic NPS question more specific, for example when seeking feedback on a certain product or service. This can be done by simply replacing the word ‘company’ with the name of the product or service.
💡 By shifting the focus of the feedback onto the specific product, you can garner invaluable information on a product that has just been released, upgraded or promoted. This is particularly useful for product managers to take into consideration when working on refining the product in question.
Qualitative, open-ended questions
The open-ended questions need to take into account the 3 categories that customers fall into following the first rating question: Promoters, Passives and Detractors.
Most NPS services use a standard format for the open-ended, qualitative questions, but they can be customized according to the specifics and goals of the business in question.
Rather than cluttering the template with too many questions, consider the main reason for reaching out to the customer in the first place.
Make sure the NPS survey has a clearly formulated goal, in order to be able to single out the question that will bring the most actionable customer feedback.
Some important factors to take into account when preparing an NPS survey are:
- Targeted customer segment
- Touchpoint in the customer journey
- Triggering event
- Behavior over time
- Customer pain points, or the one thing that could convert them into Promoters
- Survey channel
NPS surveys are characterized by being short, easy to do and flexible, and as a result this type of survey tends to show significantly higher response rates compared to other survey formats.
💡 Be wary of asking too many questions, this can overwhelm the customer and make them less likely to take the time to respond. Stick with the most important ones that are targeted at revealing the precise insights your business is looking for.
Here are some net promoter score survey question examples for the follow-up:
- What is the primary reason for your score?
- What’s the one thing we could do to make it better?
- How could we improve your experience?
- Which features do you use the most?
- What do you like most about [Company]?
- What do you like the least about [Company]?
- Was anything missing from your experience?
- What did we do well?
Different Types of NPS Surveys
NPS surveys are versatile, and can be measured every quarter, annually or just after a major transaction.
This brings up the question as to whether it is better to survey customers on a regular basis, for example quarterly, or after an important event or transaction.
Both have advantages and disadvantages, as well as specific characteristics in terms of learning more about the customer.
We’ll take a closer look here at the key differences between relationship and transactional NPS to understand how each method can help increase retention, generate insights into customers and enable business growth.
Transactional NPS surveys
Transactional NPS surveys are designed to assess a customer’s opinion of a specific business transaction.
Your company might send a Net Promoter Score survey immediately after a client places an order, and in this case the survey is designed to specifically measure satisfaction after a recent interaction with a product or service.
Transactional NPS surveys will use specific wording that mentions the transaction, for example asking the customer to rate the company “based on their most recent purchase or order”, rather than rating the business in general.
The customer’s perception of the company will be determined by singular interactions, and will change following touchpoints, such as talking to customer support or placing a new order.
Carrying out an NPS survey after such interactions will help a business understand what exactly causes a change in customer sentiment, and therefore acknowledge the positive effect or lead to fixing an issue.
Relationship
Also known as on-demand or regular NPS, Relationship NPS is designed to assess the relationship of your business with its customers. It’s the starting point for measuring customer satisfaction and identifying areas which need attention.
Using Relationship NPS surveys is more about deciding which customer segment to survey and the appropriate time to do it. Segmenting clients into clusters is the most efficient way to use relationship NPS.
In terms of timing, most businesses will send recurring surveys at standard intervals, such as quarterly or bi-annually.
Relationship surveys are not tied to a specific event, so are ideal for generating feedback on the strength of the relationship with customers.
Relationship NPS surveys tend to use general, nonspecific language that doesn’t mention a specific purchase or event.
Steps to Implement NPS Survey System
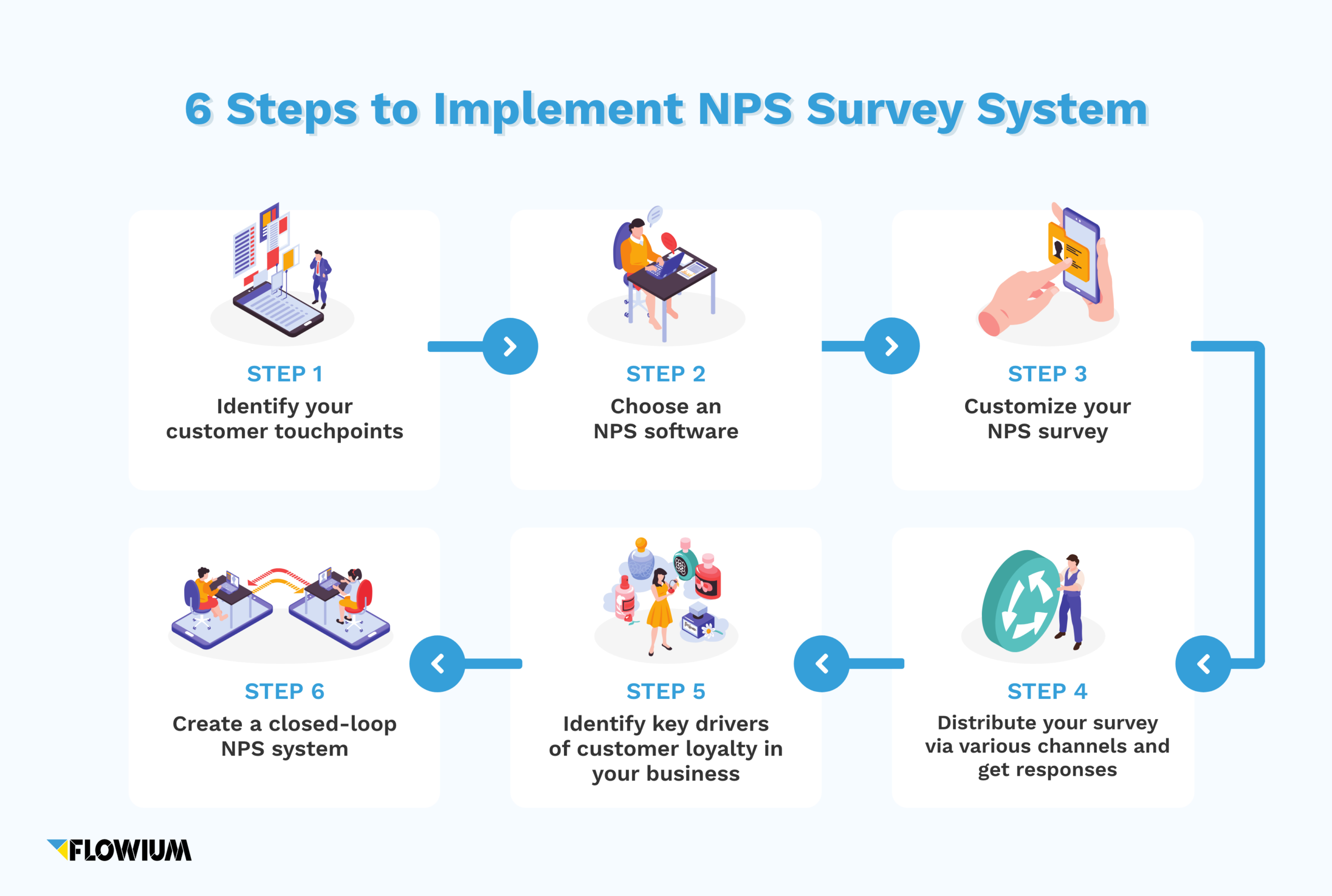
Identify your customer touchpoints
The first stage of implementing an NPS survey system is understanding the contact or touchpoints, and how they impact the customer and their experience.
Depending on whether you wish to measure transactional or relationship NPS, you may need to use different customer touchpoints in order to achieve accurate results.
Some examples of transactional NPS touchpoints:
- Post-purchase email
- Sales survey
- After-purchase prompt
- After customer service prompt
- After customer service email
- Pop-up message for web visitors
- Comment card
- Reward email
- Kiosk in store
Some examples of relationship NPS touchpoints:
- Annual survey
- Survey in-app
- Mailing
- Event comment card
- Giveaway
By choosing the right NPS touchpoints, you can reach your customers at the right time and get the information you’re looking for.
Choose an NPS software
NPS software is a survey tool that can be used to capture and analyze NPS responses on digital channels.
NPS software will show NPS responses in real-time, store those results, create reports and identify trends.
Good NPS software will make collecting, analyzing and actioning customer feedback more streamlined and sophisticated.
The right NPS software will allow you to:
- Create NPS surveys easily
- Send surveys across multiple channels
- Measure both relationship and transactional NPS
- Target different audiences
- Conduct multiple surveys at the same time
- Analyze and report the results
There are 7 key features to look for when choosing NPS software:
- Customization: The ability to customize your survey gives you more control over what customers receive and you are likely to get better response rates.
- Varied Distribution Channels: Using different channels helps gather feedback from different stages of the customer journey.
- Qualitative Responses: Being able to ask open-ended NPS questions is an important element of the NPS process.
- Multiple Surveys and Audiences: Being able to run more than one survey simultaneously means that you can pursue different customer segments or run A/B tests.
- Deliverability: Check whether the software provider puts a cap on survey recipients, and make sure you can automate the scheduling of surveys to simplify the process.
- In-Depth Reporting: Good NPS software will have extensive analytical tools to allow the analysis of customer feedback, identify trends and report the findings.
- Integrations: NPS software that can easily be integrated with other tools will help paint a comprehensive picture of customer satisfaction, and connect the dots between different areas of the business.
Customize your NPS survey
Adding optional questions to the standard survey template will allow further insights into customer behavior.
NPS software should allow full customization of your survey and the ability to add more closed-ended questions (rating, multiple choice, nominal) or open-ended questions.
💡 A NPS survey is ideally a two-part survey, with the NPS question and the qualitative reasoning question. By customizing the survey to ask exactly what you’re looking for, you will achieve the most accurate results.
Distribute your survey via various channels and get responses
The best way to distribute an NPS Survey is to reach your customers wherever they are.
If they are in store, then kiosk surveys are ideal. If they are in touch remotely, then email or SMS surveys are preferable.
Website customers can be reached by setting up website surveys and taking feedback online.
Other options include printing QR codes to scan and give feedback, distributing survey links, using iPad, Android or Mobile surveys.
Identify key drivers of customer loyalty in your business
In order to make improvements, a business has to understand what is influencing the behaviors and sentiment of detractor, passive and promoter customers.
By conducting post-survey follow-up, you can get clarity into key drivers and behavior influencers. As a result we can effectively gain greater insight and strengthen the relationship with the customer.
Create a closed-loop NPS system
By involving front-line staff, middle management and top management, you can create an effective closed-loop NPS system.
The front-line staff and technical support staff play a key role in dealing with detractors first hand, as well as encouraging promoters. Their interactions are the most direct and influential.
Middle management plays the role of training the front-line staff and creating the right ground for improving customer experiences.
Top management is responsible for developing strategy and create a system and incentives for teams to prioritize customer experience and satisfaction.
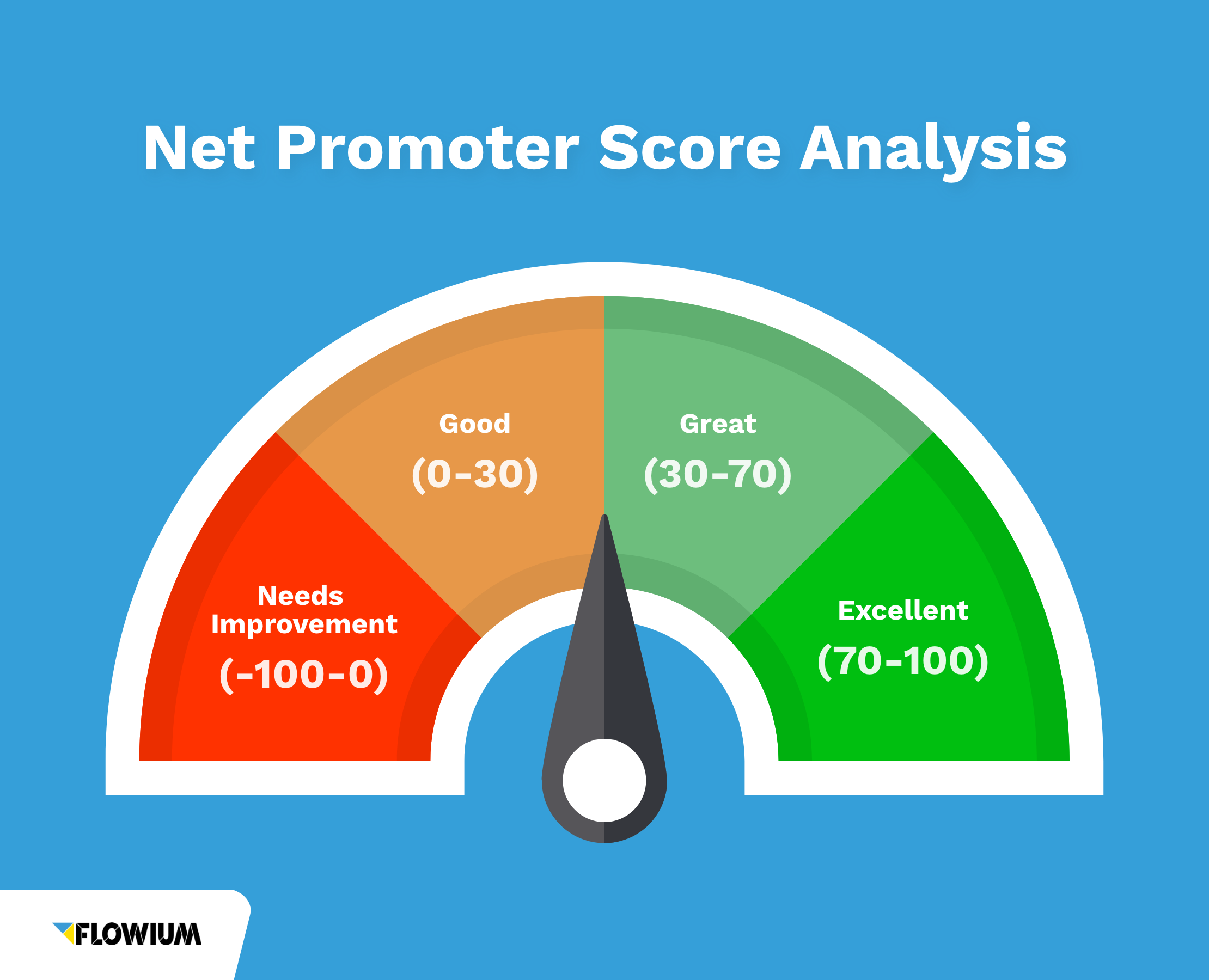
What is a good Net Promoter Score?
As a general guideline, any NPS score above 0 is ‘good’, and means that the customer base is more loyal than not. A score above 20 is considered favorable, above 50 is excellent, and above 80 is world-class.
As a rule, an NPS below 0 indicates that the business has a lot of issues to address.
Between 0 and 30 is a good net promoter score, but plenty of room for progress. A score higher than 30 indicates the company is doing well and has far more satisfied customers than unsatisfied ones.
An NPS over 70 means that the business is generating a lot of positive word-of-mouth referrals. The higher the NPS score, the more likely these customer referrals will convert into new business.
A good net promoter score depends to some degree on the industry and the country a business is based in.
Location
In Europe, customers tend to be more conservative with their ratings – a high score of 9 or 10 is rare. Japan is similar, and it is considered poor etiquette to give a perfect score.
In the US it is more common to see higher scores, with low scores being as rare as high ones are in conservative countries.
Industry
Some industries tend to lend themselves to lower NPS as a whole, such as property management and debt collection.
Check your score against net promoter score benchmarks for your specific industry to ensure this isn’t the case.
If an industry generally scores poorly, this can be an opportunity to outpace the competition by impressing even a small number of customers.
In a niche industry, it’s worth benchmarking against previous performance. You should aim to improve by about 10% per quarter to be sure of heading in the right direction.
Factors Affecting NPS Benchmarks
Primarily, there are four factors that affect NPS benchmarks:
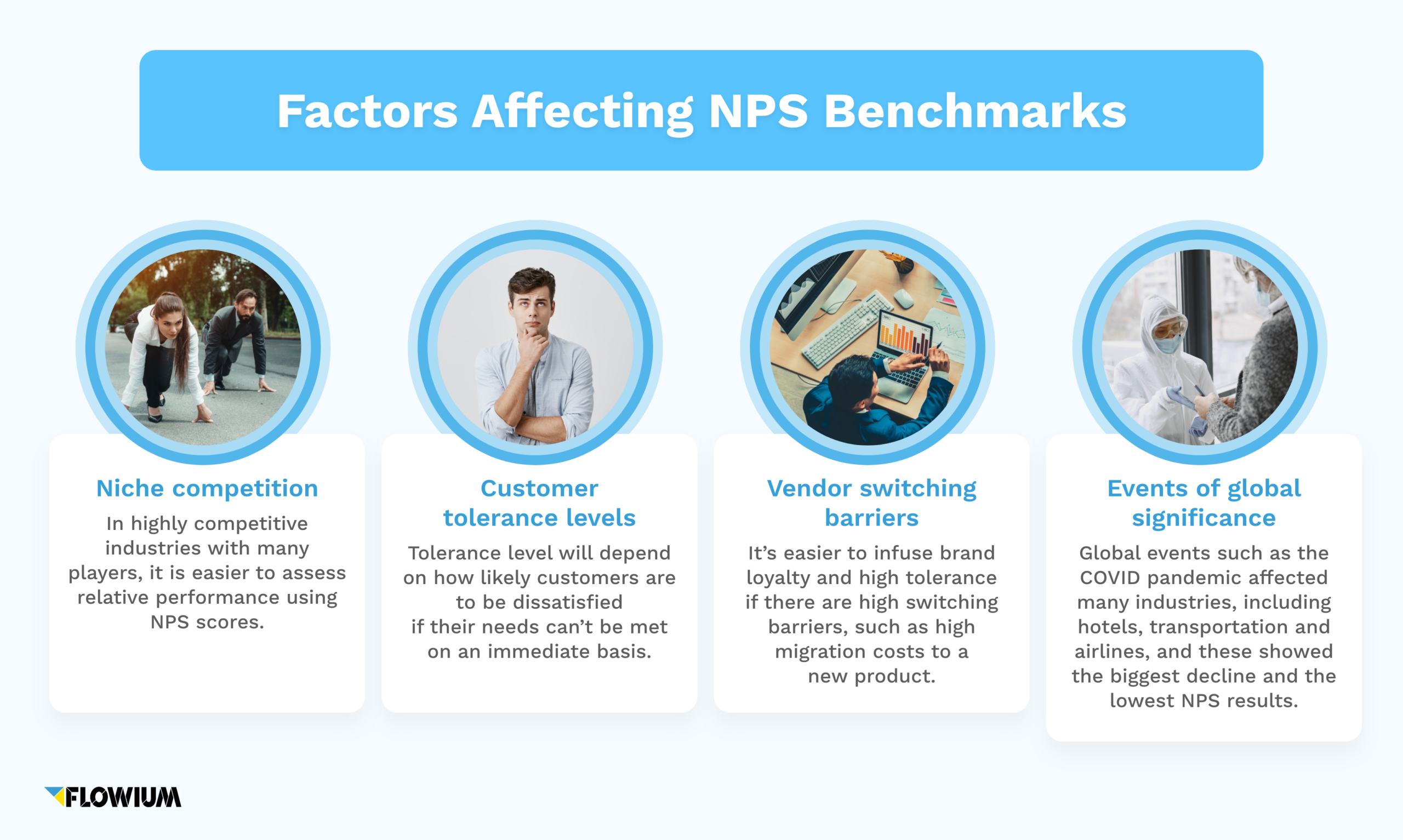
Niche competition
NPS tends to be lower in niches with fierce competition, where the customer has less tolerance for mistakes. In a less crowded niche, switching between brands can be more challenging, because of scarce competition or high-stakes purchases, and the customer will tend to rate their current choices higher.
When evaluating an NPS, consider how crowded the industry is and how unique your business, service or product is.
Customer tolerance levels
Tolerance is a crucial factor that affects net promoter score benchmarks.
Customers are likely to be influenced by how much value the business or products deliver to them day-to-day, or how much their business or life depends on it.
Tolerance level will depend on how likely customers are to be dissatisfied if their needs can’t be met on an immediate basis.
If they are likely to be swiftly unhappy, you’re in a low-tolerance industry. If not, you’re in a higher tolerance industry.
💡 Businesses can increase tolerance level by providing more customer touchpoints, greater transparency and easier accessibility.
Vendor switching barriers
It’s easier to infuse brand loyalty and high tolerance if there are high switching barriers.
Often this is a result of being unable to switch to a different brand or product without taking a financial hit, so the customer is more likely to stay consistent with their original conviction, maintaining a strong bias.
Examples of vendor switching barriers include:
- Contracts and service agreements, common in the technology industry
- Lack of viable competitors in the area, which might happen with internet providers
- Financial implications, such as buying a new car – the customer might not be completely happy, but changing product would be expensive
In these cases, it’s important for a company to focus on improving the experience for detractors, rather than focusing on the promoters.
Events of global significance
Certain events may influence results significantly, as customer interests and expectations change.
Global events such as the COVID pandemic affected many industries, including hotels, transportation and airlines, and these showed the biggest decline and the lowest NPS results.
Many companies were not ready to deal effectively with the challenges presented, leading to long waiting times, bugs, slow processing and errors that impacted overall customer satisfaction.
Things to Keep in Mind Regarding Net Promoter Score
The choice of metric is not as important as people think
Companies rarely succeed or fail based on the specific metric chosen. However, NPS is widely known to accurately correlate to customer loyalty, so clearly works.
For specific data, adding other survey methods or additional questions will always add value.
Driving improvements is what’s critical
It’s less about the metric used to acquire and measure feedback, and more about what you do with it.
Companies should think carefully about what they learn from using their chosen metric.
Promoters and detractors need individual attention
Beyond the net promoter score, you need to understand what is driving the score. Don’t just focus on fixing Detractors, understand what is driving the scores.
By analyzing what causes Promoters, you will get the opportunity to engage the business in uplifting discussions.
NPS is for relationships, not transactions
Be careful of asking customers only about the most recent interaction, as it’s more valuable to study the entire experience.
For example, if a customer generally loves the business but had a poor recent experience, the NPS score right after that interaction might be lower and not reflect the overall sentiment the customer has for the business.
It’s important to use the NPS question in the right place, at the right time and for the right reason.
NPS is for teams, not individuals
While individual employees can impact an NPS score, keep in mind that NPS asks about the likelihood to recommend a company, not an individual.
NPS isn’t used to rate an employee, but the overall experience.
FAQs about Net Promoter Score
Many companies send surveys to every customer at the same time once per quarter. However, it can be more beneficial to spread out the survey and send to 1/90th of customers every day for 90 days. If you send all surveys at once, the responses will only represent one moment in time. By spreading the surveys out, you can act on the feedback and see the score change in nearly real-time.
This depends on what you are seeking to measure: loyalty to the individual product, or loyalty to the customer in general. Most experts recommend measuring brand loyalty over individual product loyalty, therefore sending an NPS survey once per quarter. It’s often thought that surveying customers quarterly on a rolling basis is the most effective frequency that isn’t too invasive. Wait longer and you can miss critical feedback or changes in customer sentiment, send it too often and you may annoy people.
This depends on what you want to measure. Sending a survey right after a customer places an order can be an effective way to measure customer loyalty for the shopping cart process. However, if you are more interested in measuring how likely the customer is to recommend the product they purchased, schedule the survey a bit further out to give the customer time to receive and start using the product. They’ll then be able to give relevant, actionable feedback.